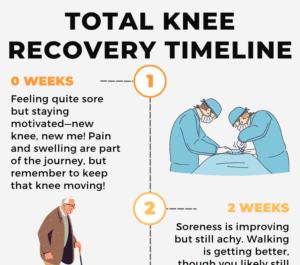
Knee replacement surgery is often seen as the ultimate solution for chronic knee pain, but is it always necessary? While it can dramatically improve quality of life for the right candidate, not everyone who undergoes the procedure is satisfied with the outcome. Let’s dive into the facts about knee replacements, explore non-surgical alternatives, and uncover factors that influence success.
Shocking Statistics About Knee Replacements
Every year, over 600,000 knee replacement surgeries are performed in the U.S., and this number is expected to rise significantly. However, studies show that up to 20% of patients are dissatisfied with their results. This raises an important question: Why are some patients unhappy?
Why Are Some Patients Unhappy With Knee Replacements?
Limitations of Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement isn’t a cure-all. Some patients experience:
Residual pain or stiffness.
Limited range of motion despite successful surgery.
Ongoing functional challenges.
Identifying Inappropriate Candidates for Surgery
Certain factors can make knee replacement less effective:
Mild to moderate arthritis that might be managed conservatively.
Coexisting health conditions that complicate recovery.
Unrealistic expectations about the surgery’s outcomes.
Who Should Consider a Knee Replacement?
Knee replacement might be appropriate if you:
Have severe arthritis or joint damage confirmed by imaging.
Experience debilitating pain that disrupts daily activities.
Have not responded to non-surgical treatments like medication or physical therapy.
However, even for these cases, a thorough evaluation by a specialist is crucial to determine if surgery is truly the best option.
Non-Surgical Alternatives to Knee Replacements
Before committing to surgery, consider these alternatives:
Physical Therapy: Strengthening surrounding muscles to improve joint stability.
Injections: Corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
Weight Management: Reducing stress on the knee joint through a healthy weight.
Bracing or Orthotics: Providing additional support to the knee.
Medications: NSAIDs or other pain relievers to manage symptoms.
These options can often delay or even eliminate the need for surgery.
Making an Informed Decision
Deciding on knee replacement surgery is a personal and complex choice. Ask yourself:
Have I exhausted all non-surgical options?
Am I prepared for the recovery process?
Do I fully understand the potential risks and benefits?
Your healthcare provider can guide you through these questions to ensure the decision aligns with your goals and needs.